I/O控制方式
本文共 965 字,大约阅读时间需要 3 分钟。
I/O控制方式
程序直接控制方式
CPU干预
很频繁,I/O操作开始之前,完成之后需要CPU介入,而且在等待I/O完成的过程中CPU需要不断得轮询检查。
数据的流向
每次读/写一个字
读操作(数据输入):I/O设备->CPU->内存 写操作(数据输出):内存->CPU->I/O设备流程图
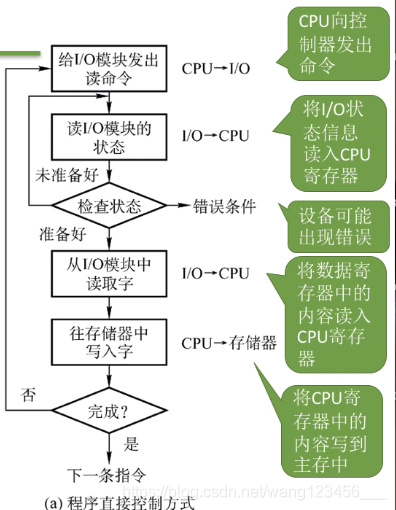
主要缺点和主要优点
优点:实现简单。在读/写指令之后,加上实现循环检查的一系列指令即可(因此才称为“程序直接控制方式”)
缺点:CPU和1/0设备只能串行工作,CPU需要一直轮询检查长期处于“忙等”状态,CPU利用率低。中断驱动方式
CPU干预
每次1/0操作开始之前、完成之后需要CPU介入。等待1/0完成的过程中CPU可以切换到别的进程执行。
数据的流向
每次读/写一个字
读操作(数据输入): I/0设备->CPU->内存 写操作(数据输出): 内存->CPU->I/0设备流程图
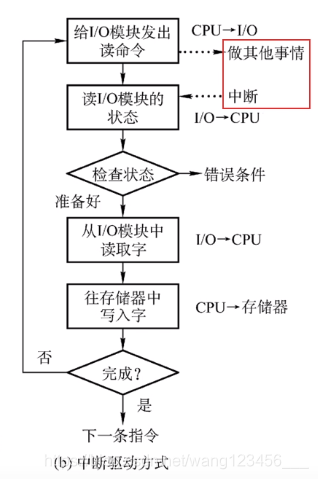
主要缺点和主要优点
优点:与“程序直接控制方式”相比,在“中断驱动方式”中,1/0控制器会通过中断信号主动报告1/0已完成,CPU不再需要不停地轮询。 CPU和1/0设备可并行工作,CPU利用率得到明显提升。
缺点:每个字在I/O设备与内存之间的传输,都需要经过CPU。而频繁的中断处理会消耗比较多的CPU时间。DMA方式
CPU干预
仅在传送一个或多个数据块的开始和结束时,才需要CPU干预
数据的流向
每次读/写一个块
读操作(数据输入): I/0设备->内存 写操作(数据输出): 内存->I/0设备流程图

主要缺点和主要优点
优点:数据传输以“块”为单位,CPU介入频率进一步降低。数据的传输不再需要先经过CPU再写入内存,数据传输效率进一步增加。CPU和1/0设备的并行性得到提升。
缺点:CPU每发出一条1/0指令,只能读/写一个或多个连续的数据块。通道控制方式
CPU干预
极低,通道会根据CPU的指示执行相应的通道程序,只有完成一组数据块的读/写后才需要发出中断信号,请求CPU干预。
数据的流向
每次读/写一组数据块
读操作(数据输入):I/0设备->内存 写操作(数据输出):内存->I/0设备流程图

主要缺点和主要优点
缺点:实现复杂,需要专门的通道硬件支持
优点:CPU、通道、1/0设备可并行工作,资源利用率很高转载地址:http://uudzz.baihongyu.com/
你可能感兴趣的文章
MySQL原理简介—10.SQL语句和执行计划
查看>>
MySQL原理简介—11.优化案例介绍
查看>>
MySQL原理简介—12.MySQL主从同步
查看>>
MySQL原理简介—2.InnoDB架构原理和执行流程
查看>>
MySQL原理简介—3.生产环境的部署压测
查看>>
MySQL原理简介—6.简单的生产优化案例
查看>>
MySQL原理简介—7.redo日志的底层原理
查看>>
MySQL原理简介—8.MySQL并发事务处理
查看>>
MySQL原理简介—9.MySQL索引原理
查看>>
MySQL参数调优详解
查看>>
mysql参考触发条件_MySQL 5.0-触发器(参考)_mysql
查看>>
MySQL及navicat for mysql中文乱码
查看>>
MySqL双机热备份(二)--MysqL主-主复制实现
查看>>
MySQL各个版本区别及问题总结
查看>>
MySql各种查询
查看>>
mysql同主机下 复制一个数据库所有文件到另一个数据库
查看>>
mysql启动以后会自动关闭_驾照虽然是C1,一直是开自动挡的车,会不会以后就不会开手动了?...
查看>>
mysql启动和关闭外键约束的方法(FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS)
查看>>
Mysql启动失败解决过程
查看>>
MySQL启动失败:Can't start server: Bind on TCP/IP port
查看>>